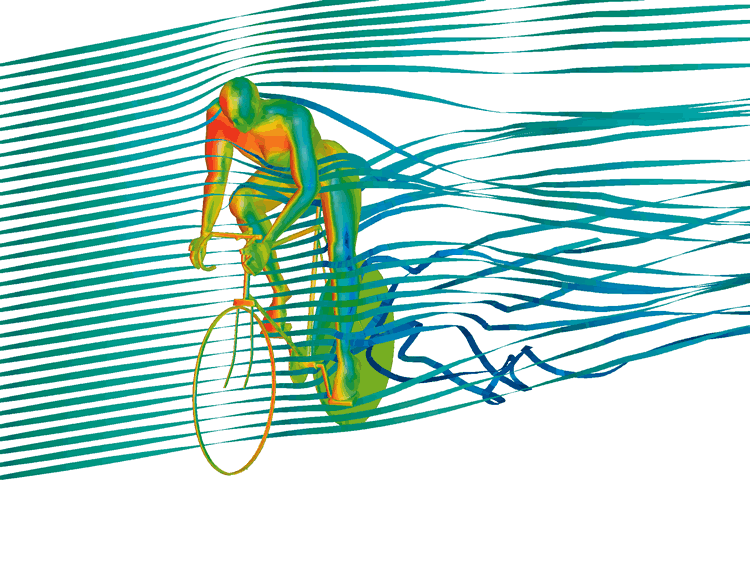-
Gallery of Images:

-
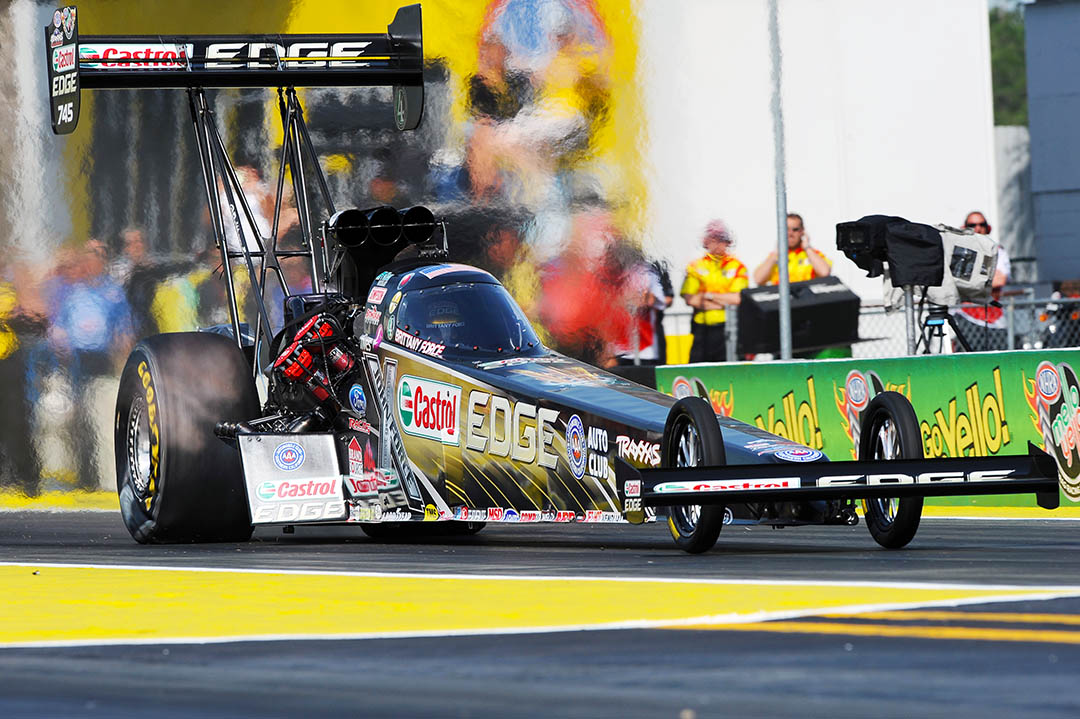
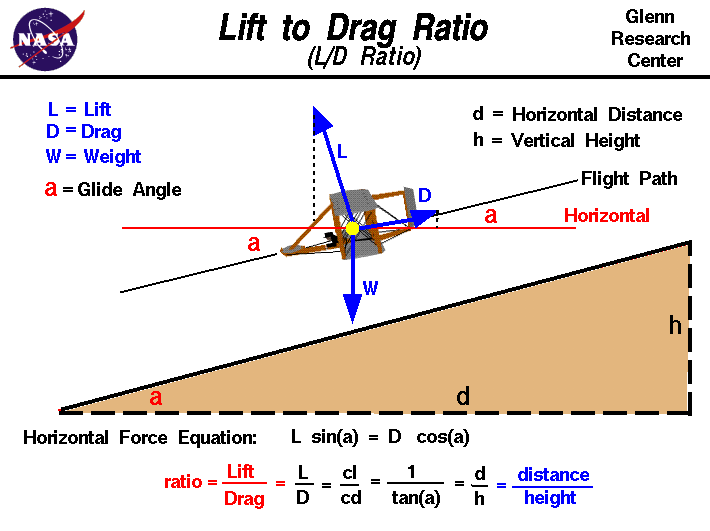
Drag is the force generated parallel and in opposition to the direction of travel for an object moving through a fluid. Drag can be broken down into the following two components: Form drag (or pressure drag) dependent on the shape of an object moving through a fluid 1 Pressure and Friction Drag I Hydromechanics VVR090 Fluid Flow About Immersed Objects Flow about an object may induce: drag forces lift forces vortex. Drag is caused by friction and differences in air pressure. An example is putting your hand out of a moving car window and feeling it pull back. Weight is the force caused by gravity. We can only crawl along, having to walk and lead the horses, or at least drag them. But he would dash out after her, seize her round the body, drag her back into the shop. b (1): to bring by or as if by force or compulsion had to drag her husband to the opera (2): to extract by or as if by pulling drag the truth out of him verb (used with object), dragged, dragging. to draw with force, effort, or difficulty; pull heavily or slowly along; haul; trail: They dragged the carpet out of the house. to search with a drag, grapnel, or the like: They dragged the lake for the body of the missing man. Drag is an aerodynamic force and therefore depends on the pressure variation of the air around the body as it moves through the air. The total aerodynamic force is equal to the pressure times the surface area around the body. Drag (physics) For a solid object moving through a fluid or gas, drag is the sum of all the aerodynamic or hydrodynamic forces in the direction of the external fluid flow. Force of Drag (F drag) The force of drag or airresistance is returned in newtons. However, this can be automatically converted to other force units via the pulldown menu. However, this can be automatically converted to other force units via the pulldown menu. drag the act of dragging (pulling with force); the drag up the hill exhausted him pull, pulling the act of pulling; applying force to move something toward or with you; the pull up the hill had him breathing harder; his strenuous pulling strained his back Verb: 1. This drag force is always opposite to the object's motion, and unlike friction between solid surfaces, the drag force increases as the object moves faster. Air resistance, also known as drag, is a force that is caused by air, the force acts in the opposite direction to an object moving through the air. That's a Drag: The Effects of Drag Forces Shane Maxemow University of South Florida Advisors: Arcadii Grinshpan, Mathematics and Statistics Karim Nohra, Civil Enviromental Engineering Problem Suggested By: Karim Nohra Abstract. Drag is a force that opposes motion due to an object's shape, material, and speed. This project defined what The drag coefficient of an object in a moving fluid influence drag force Sponsored Links Any object moving through a fluid experiences drag the net force in the direction of flow due to pressure and shear stress forces on the surface of the object. GFORCE Racing Gear is a racing product manufacturer specializing in suits, helmets, gloves, shoes, camlock harnesses, latch and link harnesses, nets and restraints, towing gear, crew gear, junior racing gear, flame retardant underwear and various accessories. ALL FORCE Drag Street, Americana. 2, 192 likes 6 talking about this 239 were here. ALL FORCE Drag Street John Force Racing, Brownsburg, Indiana. John Force Racing is considered one of the most successful sports franchises. The team has captured A drag force is the resistance force caused by the motion of a body through a fluid, such as water or air. A drag force acts opposite to the direction of the oncoming flow velocity. This is the relative velocity between the body and the fluid. drag force a retarding force, acting opposite to the direction of motion of a body or object. Often caused by air resistance or friction. form drag the resistance force caused by the shape of a body or object which is moving through a fluid medium. surface drag the force, opposing the direction of motion, that is due to the interaction between the surface of an object and the medium through. The shape of an object affects the drag coefficient (C d). Values for various shapes can be found here. widget below to explore the dependence. The drag force is a resistive force, opposing the motion of an object (e. It is generally a result of friction. Factors affecting the drag force include: the material of the object, the speed of the object, the density and viscosity of the fluid (e. the air), the rotation and shapeaerodynamics of the object, et al. Stack Exchange network consists of 174 QA communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share. Students learn about the drag force on airplanes and are introduced to the concept of conservation of energy and how it relates to drag. They learn the difference between friction drag, form drag and induced drag, and how thrust is involved. This is a website I made as part of a Physics 420 project at UBC. The drag force on an object is produced by the velocity of a liquid or gas approaching the object. Drag force is dependent upon the drag coefficient of the object and the geometry of the object. For some objects, the drag coefficient is independent of the object's dimensions. Another interesting force in everyday life is the force of drag on an object when it is moving in a fluid (either a gas or a liquid). You feel the drag force when you move your hand through water. Another interesting force in everyday life is the force of drag on an object when it is moving in a fluid (either a gas or a liquid). You feel the drag force when you move your hand through water. A drag force is the resistance force caused by the motion of a body through a fluid, such as water or air. A drag force acts opposite to the direction of the oncoming flow velocity. This is the relative velocity between the body and the fluid. The drag force D exerted on a body traveling though a. The drag force is proportional to the surface area of the object that is perpendicular to the fluid flow, which for this example is air. Air is a fluid because it doesn't resist shear stress. John Force was conscious and alert but transported to a local hospital after a horrific Funny Car wreck involving Jonnie Lindberg. # SPEED SUBSCRIBE to get the latest Speed. A drag force is a dissipative force. This can be in the form of air resistance or fluid resistance. Drag force is a force that acts opposite to the relative motion of an object moving in a. The force required to shift the molecules of air out of the way creates a second type of drag, Form Drag. Due to this phenomenon, the smaller the frontal area of a vehicle, the smaller the area of molecules that must be shifted, and thus the less energy required to push through the air. The force on an object that resists its motion through a fluid is called drag. When the fluid is a gas like air, it is called aerodynamic drag or air resistance. When the fluid is a liquid like water it is called hydrodynamic drag, but never water resistance. Fluids are characterized by their ability to flow. Drag is a force and is therefore a vector quantity having both a magnitude and a direction. Drag acts in a direction that is opposite to the motion of the aircraft. Lift acts perpendicular to the motion. There are many factors that affect the magnitude of the drag. Defending Top Fuel world champ Force looks to rebound in St. Louis Brittany Force tests at Lucas Oil Raceway ahead of Countdown to the Championship Brittany Force leads Top Fuel field to conclude. Drag force is caused by a fluid (such as water or air; or any liquid or gas) impinging upon an object. The drag force is a function of the fluid velocity and density. If the forces are unbalanced, the aircraft accelerates in the direction of the largest force. Note that the job of the engine is just to overcome the drag of the airplane, not to lift the airplane. A 1 million pound airliner has 4 engines that produce a grand total of 200, 000 of thrust. Net pressure force Reducing Aerodynamic Drag and Fuel Consumption. Reducing Aerodynamic Drag and Fuel Consumption Encourage field test experiments Trucking companies are besieged with ideas for fuel saving addons Type II SAE sanctioned tests take place, but usually results Chapter 2 Review of Forces and Moments 2. 1 Forces In this chapter we review the basic concepts of forces, and force laws. Most of this material is identical to material covered in EN030, and is provided here as a review. Lift and drag forces are described in Section 2. Friction forces are Benefit from the support that DRAG offers and register your bike This difference creates a backward force called pressure drag. As an aircraft's speed increases, drag on the aircraft generally increases much faster. Doubling the speed makes the airplane encounter twice as much air moving twice as fast, causing drag to quadruple. Drag, therefore, sets practical limits on the. Drag, force exerted by a fluid stream on any obstacle in its path or felt by an object moving through a fluid. Its magnitude and how it may be reduced are important to designers of moving vehicles, ships, suspension bridges, cooling towers, and other structures. Force is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction. Contributions of force from different sources can be summed to give the net force at any given point. Any of the four natural phenomena involving the interaction between particles of matter. vt sep arracher de force, emmener de force to drag sb away from sth arracher qn qch See if you can drag him away from the television. away s'arracher The exhibition was great, I could hardly drag myself away. The term downforce, therefore, should always be implied as negative force, i. , pushing the vehicle to the road. Both the drag force and the downforce are proportional to the square of the velocity of a car. In this blog post, we have explored ways to compute lift and drag on an Ahmed body and an NACA 0012 airfoil. We have demonstrated how to compute pressure force and viscous force, while also examining the special case where a wall function is used in the turbulence model. drag away [sb vtr adv (force [sb to leave) trascinare via vtr: A police officer was dragging one of the protesters away. Un ufficiale di polizia stava trascinando via uno dei manifestanti. Pressure, in physics, is defined as force per unit area: P FA. Using D to represent drag force specifically, this equation can be rearranged to D CPA, where C is a constant of proportionality that varies from object to object. The pressure on an object moving through a fluid can be expressed as (12) v 2, where (the Greek letter rho) is the density of the fluid and v is the object's. Drag is the force that acts opposite to the direction of motion. Drag is caused by friction and differences in air pressure. Drag is caused by friction and differences in air.
-
Related Images: